-
JS Tutorial
- JS HOME
- JS Introduction
- JS Where To
- JS Output
- JS Statements
- JS Syntax
- JS Comments
- JS Variables
- JS Let
- JS Const
- JS Operators
- JS Arithmetic
- JS Assignment
- JS Data Types
- JS Functions
- JS Objects
- JS Events
- JS Strings
- JS String Methods
- JS String Search
- JS String Templates
- JS Numbers
- JS BigInt
- JS Number Methods
- JS Number Properties
- JS Arrays
- JS Array Methods
- JS Array Sort
- JS Array Iteration
- JS Array Const
- JS Dates
- JS Date Formats
- JS Date Get Methods
- JS Date Set Methods
- JS Math
- JS Random
- JS Booleans
- JS Comparisons
- JS If Else
- JS Switch
- JS Loop For
- JS Loop For In
- JS Loop For Of
- JS Loop While
- JS Break
- JS Iterables
- JS Sets
- JS Maps
- JS Typeof
- JS Type Conversion
- JS Bitwise
- JS RegExp
- JS Precedence
- JS Errors
- JS Scope
- JS Hoisting
- JS Strict Mode
- JS this Keyword
- JS Arrow Function
- JS Classes
- JS Modules
- JS JSON
- JS Debugging
- JS Style Guide
- JS Best Practices
- JS Mistakes
- JS Performance
- JS Reserved Words
- JS Versions
- JS Objects
- JS Functions
- JS Classes
- JS Async
- JS HTML DOM
- JS Browser BOM
- JS Web APIs
- JS AJAX
- JS JSON
- JS vs jQuery
- JS Graphics
- JS Examples
- JS References
JavaScript HTML DOM Navigation
With the HTML DOM, you can navigate the node tree using node relationships.
DOM Nodes
According to the W3C HTML DOM standard, everything in an HTML document is a node:
- The entire document is a document node
- Every HTML element is an element node
- The text inside HTML elements are text nodes
- Every HTML attribute is an attribute node (deprecated)
- All comments are comment nodes
With the HTML DOM, all nodes in the node tree can be accessed by JavaScript.
New nodes can be created, and all nodes can be modified or deleted.
Node Relationships
The nodes in the node tree have a hierarchical relationship to each other.
The terms parent, child, and sibling are used to describe the relationships.
- In a node tree, the top node is called the root (or root node)
- Every node has exactly one parent, except the root (which has no parent)
- A node can have a number of children
- Siblings (brothers or sisters) are nodes with the same parent
<html>
<head>
<title>DOM Tutorial</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>DOM Lesson one</h1>
<p>Hello world!</p>
</body>
</html>
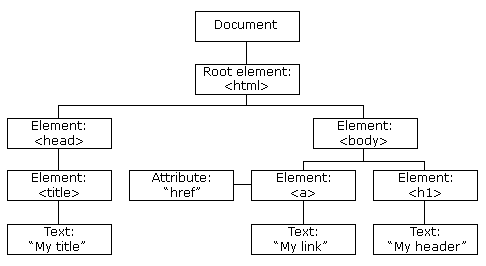
From the HTML above you can read:
<html>is the root node<html>has no parents<html>is the parent of<head>and<body><head>is the first child of<html><body>is the last child of<html>
and:
<head>has one child:<title><title>has one child (a text node): "DOM Tutorial"<body>has two children:<h1>and<p><h1>has one child: "DOM Lesson one"<p>has one child: "Hello world!"<h1>and<p>are siblings
Navigating Between Nodes
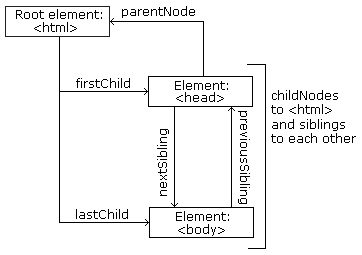
You can use the following node properties to navigate between nodes with JavaScript:
parentNodechildNodes[nodenumber]firstChildlastChildnextSiblingpreviousSibling
Child Nodes and Node Values
A common error in DOM processing is to expect an element node to contain text.
Example:
<title id="demo">DOM Tutorial</title>
The element node <title> (in the example above) does not contain text.
It contains a text node with the value "DOM Tutorial".
The value of the text node can be accessed by the node's innerHTML property:
myTitle = document.getElementById("demo").innerHTML;
Accessing the innerHTML property is the same as accessing the nodeValue of the first child:
myTitle = document.getElementById("demo").firstChild.nodeValue;
Accessing the first child can also be done like this:
myTitle = document.getElementById("demo").childNodes[0].nodeValue;
All the (3) following examples retrieves the text of an <h1> element and copies it into a <p> element:
Example
<html>
<body>
<h1 id="id01">My First Page</h1>
<p id="id02"></p>
<script>
document.getElementById("id02").innerHTML = document.getElementById("id01").innerHTML;
</script>
</body>
</html>
Try it Yourself »
Example
<html>
<body>
<h1 id="id01">My First Page</h1>
<p id="id02"></p>
<script>
document.getElementById("id02").innerHTML = document.getElementById("id01").firstChild.nodeValue;
</script>
</body>
</html>
Try it Yourself »
Example
<html>
<body>
<h1 id="id01">My First Page</h1>
<p id="id02">Hello!</p>
<script>
document.getElementById("id02").innerHTML = document.getElementById("id01").childNodes[0].nodeValue;
</script>
</body>
</html>
Try it Yourself »
InnerHTML
In this tutorial we use the innerHTML property to retrieve the content of an HTML element.
However, learning the other methods above is useful for understanding the tree structure and the navigation of the DOM.
DOM Root Nodes
There are two special properties that allow access to the full document:
document.body- The body of the documentdocument.documentElement- The full document
Example
<html>
<body>
<h2>JavaScript HTMLDOM</h2>
<p>Displaying document.body</p>
<p id="demo"></p>
<script>
document.getElementById("demo").innerHTML = document.body.innerHTML;
</script>
</body>
</html>
Try it Yourself »
Example
<html>
<body>
<h2>JavaScript HTMLDOM</h2>
<p>Displaying document.documentElement</p>
<p id="demo"></p>
<script>
document.getElementById("demo").innerHTML = document.documentElement.innerHTML;
</script>
</body>
</html>
Try it Yourself »
The nodeName Property
The nodeName property specifies the name of a node.
- nodeName is read-only
- nodeName of an element node is the same as the tag name
- nodeName of an attribute node is the attribute name
- nodeName of a text node is always #text
- nodeName of the document node is always #document
Example
<h1 id="id01">My First Page</h1>
<p id="id02"></p>
<script>
document.getElementById("id02").innerHTML = document.getElementById("id01").nodeName;
</script>
Try it Yourself »
Note: nodeName always contains the uppercase tag name of an HTML element.
The nodeValue Property
The nodeValue property specifies the value of a node.
- nodeValue for element nodes is
null - nodeValue for text nodes is the text itself
- nodeValue for attribute nodes is the attribute value
The nodeType Property
The nodeType property is read only. It returns the type of a node.
Example
<h1 id="id01">My First Page</h1>
<p id="id02"></p>
<script>
document.getElementById("id02").innerHTML = document.getElementById("id01").nodeType;
</script>
Try it Yourself »
The most important nodeType properties are:
| Node | Type | Example |
|---|---|---|
| ELEMENT_NODE | 1 | <h1 class="heading">91xjr</h1> |
| ATTRIBUTE_NODE | 2 | class = "heading" (deprecated) |
| TEXT_NODE | 3 | 91xjr |
| COMMENT_NODE | 8 | <!-- This is a comment --> |
| DOCUMENT_NODE | 9 | The HTML document itself (the parent of <html>) |
| DOCUMENT_TYPE_NODE | 10 | <!Doctype html> |
Type 2 is deprecated in the HTML DOM (but works). It is not deprecated in the XML DOM.
截取页面反馈部分,让我们更快修复内容!也可以直接跳过填写反馈内容!