Pattern Recognition
Neural Networks are used in applications like Facial Recognition.
These applications use Pattern Recognition.
This type of Classification can be done with a Perceptron.
Perceptrons can be used to classify data into two parts.
Perceptrons are also known as a Linear Binary Classifiers.
Pattern Classification
Imagine a strait line (a linear graph) in a space with scattered x y points.
How can you classify the points over and under the line?
A perceptron can be trained to recognize the points over the line, without knowing the formula for the line.
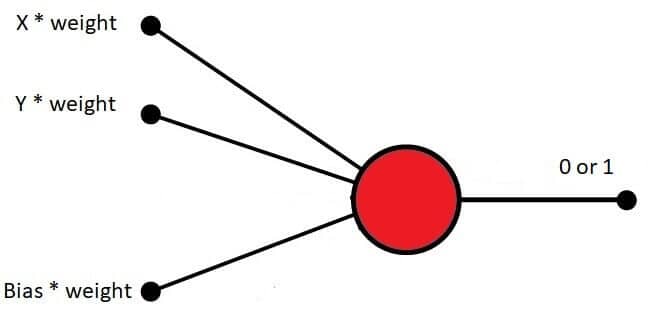
How to Program a Perceptron
To program a perceptron, we can use a simple JavaScript program that will:
- Create a simple plotter
- Create 500 random x y points
- Display the x y points
- Create a line function: f(x)
- Display the line
- Compute the desired answers
- Display the desired answers
Create a Simple Plotter
Creating a simple plotter object is described in the AI Canvas Chapter.
Example
const plotter = new XYPlotter("myCanvas");
plotter.transformXY();
const xMax = plotter.xMax;
const yMax = plotter.yMax;
const xMin = plotter.xMin;
const yMin = plotter.yMin;
Create Random X Y Points
Create as many xy points as wanted.
Let the x values be random (between 0 and maximum).
Let the y values be random (between 0 and maximum).
Display the points in the plotter:
Example
const numPoints = 500;
const xPoints = [];
const yPoints = [];
for (let i = 0; i < numPoints; i++) {
xPoints[i] = Math.random() * xMax;
yPoints[i] = Math.random() * yMax;
}
Create a Line Function
Display the line in the plotter:
Compute Correct Answers
Compute the correct answers based on the line function:
y = x * 1.2 + 50.
The desired answer is 1 if y is over the line and 0 if y is under the line.
Store the desired answers in an array (desired[]).
Example
let desired = [];
for (let i = 0; i < numPoints; i++) {
desired[i] = 0;
if (yPoints[i] > f(xPoints[i])) {desired[i] = 1;}
}
Display the Correct Answers
For each point, if desired[i] = 1 display a black point, else display a blue point.
Example
for (let i = 0; i < numPoints; i++) {
let color = "blue";
if (desired[i]) color = "black";
plotter.plotPoint(xPoints[i], yPoints[i], color);
}
How to Train a Perceptron
In the next chapter, you will learn how to use the correct answers to:
Train a perceptron to predict the output values of unknown input values.
截取页面反馈部分,让我们更快修复内容!也可以直接跳过填写反馈内容!