XML DOM - Navigating Nodes
Nodes can be navigated using node relationships.
Navigating DOM Nodes
Accessing nodes in the node tree via the relationship between nodes, is often called "navigating nodes".
In the XML DOM, node relationships are defined as properties to the nodes:
- parentNode
- childNodes
- firstChild
- lastChild
- nextSibling
- previousSibling
The following image illustrates a part of the node tree and the relationship between nodes in books.xml:
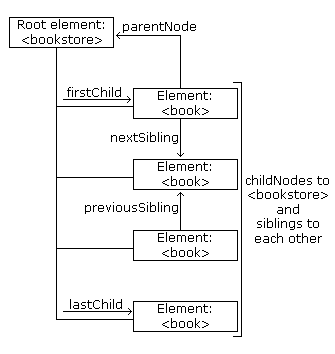
DOM - Parent Node
All nodes have exactly one parent node. The following code navigates to the parent node of <book>:
Example
function myFunction(xml) {
var xmlDoc = xml.responseXML;
var x = xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName("book")[0];
document.getElementById("demo").innerHTML = x.parentNode.nodeName;
}
Try it Yourself »
Example explained:
- Load books.xml into xmlDoc
- Get the first <book> element
- Output the node name of the parent node of "x"
Avoid Empty Text Nodes
Some browsers might treat empty white-spaces or new lines as text nodes. This causes a problem when using the properties: firstChild, lastChild, nextSibling, previousSibling.
To avoid navigating to empty text nodes (spaces and new-line characters between element nodes), we use a function that checks the node type:
function get_nextSibling(n) {
var y = n.nextSibling;
while (y.nodeType != 1) {
y = y.nextSibling;
}
return y;
}
The function above allows you to use get_nextSibling(node) instead of the property node.nextSibling.
Code explained:
Element nodes are type 1. If the sibling node is not an element node, it moves to the next nodes until an element node is found.
Get the First Child Element
The following code displays the first element node of the first <book>:
Example
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<p id="demo"></p>
<script>
var xhttp = new XMLHttpRequest();
xhttp.onreadystatechange = function() {
if (this.readyState == 4 && this.status == 200) {
myFunction(this);
}
};
xhttp.open("GET", "books.xml", true);
xhttp.send();
function myFunction(xml) {
var xmlDoc = xml.responseXML;
var x = get_firstChild(xmlDoc.getElementsByTagName("book")[0]);
document.getElementById("demo").innerHTML = x.nodeName;
}
//check if the first node is an element node
function get_firstChild(n) {
var y = n.firstChild;
while (y.nodeType != 1) {
y = y.nextSibling;
}
return y;
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
Output:
title
Try it Yourself »
Example explained:
- Load books.xml into xmlDoc
- Use the get_firstChild function on the first <book> element node to get the first child node that is an element node
- Output the node name of first child node that is an element node
More Examples
lastChild()
Use the lastChild() method and a custom function to get the last child node of a node.
nextSibling()
Use the nextSibling() method and a custom function to get the next sibling node of a node.
previousSibling()
Use the previousSibling() method and a custom function to get the previous sibling node of a node.
截取页面反馈部分,让我们更快修复内容!也可以直接跳过填写反馈内容!