C# Multidimensional Arrays
Multidimensional Arrays
In the previous chapter, you learned about arrays, which is also known as single dimension arrays. These are great, and something you will use a lot while programming in C#. However, if you want to store data as a tabular form, like a table with rows and columns, you need to get familiar with multidimensional arrays.
A multidimensional array is basically an array of arrays.
Arrays can have any number of dimensions. The most common are two-dimensional arrays (2D).
Two-Dimensional Arrays
To create a 2D array, add each array within its own set of curly braces, and insert a comma (,) inside the square brackets:
Example
int[,] numbers = { {1, 4, 2}, {3, 6, 8} };
Good to know: The single comma [,] specifies that the array is two-dimensional. A three-dimensional array would have two commas: int[,,].
numbers is now an array with two arrays as its elements. The first array element contains three elements: 1, 4 and 2, while the second array element contains 3, 6 and 8. To visualize it, think of the array as a table with rows and columns:
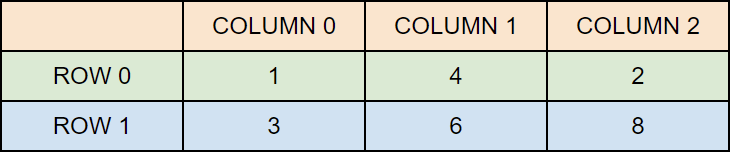
Access Elements of a 2D Array
To access an element of a two-dimensional array, you must specify two indexes: one for the array, and one for the element inside that array. Or better yet, with the table visualization in mind; one for the row and one for the column (see example below).
This statement accesses the value of the element in the first row (0) and third column (2) of the numbers array:
Example
int[,] numbers = { {1, 4, 2}, {3, 6, 8} };
Console.WriteLine(numbers[0, 2]); // Outputs 2Remember that: Array indexes start with 0: [0] is the first element. [1] is the second element, etc.
Change Elements of a 2D Array
You can also change the value of an element.
The following example will change the value of the element in the first row (0) and first column (0):
Example
int[,] numbers = { {1, 4, 2}, {3, 6, 8} };
numbers[0, 0] = 5; // Change value to 5
Console.WriteLine(numbers[0, 0]); // Outputs 5 instead of 1Loop Through a 2D Array
You can easily loop through the elements of a two-dimensional array with a foreach loop:
Example
int[,] numbers = { {1, 4, 2}, {3, 6, 8} };
foreach (int i in numbers)
{
Console.WriteLine(i);
} You can also use a for loop. For multidimensional arrays, you need one loop for each of the array's dimensions.
Also note that we have to use GetLength() instead of Length to specify how many times the loop should run:
Example
int[,] numbers = { {1, 4, 2}, {3, 6, 8} };
for (int i = 0; i < numbers.GetLength(0); i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < numbers.GetLength(1); j++)
{
Console.WriteLine(numbers[i, j]);
}
} 截取页面反馈部分,让我们更快修复内容!也可以直接跳过填写反馈内容!